Mode localization in weakly coupled microelectromechanical resonators
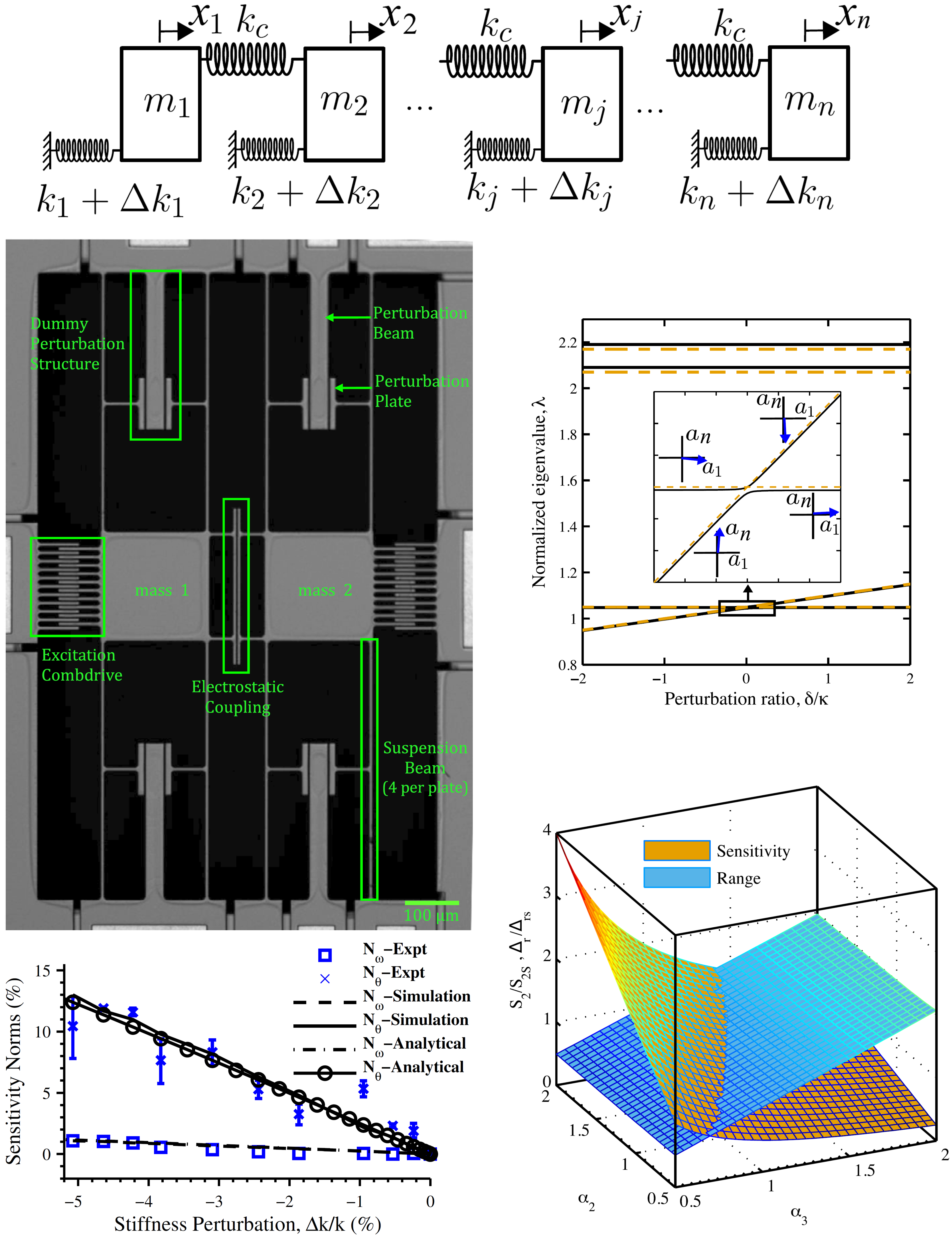 Weakly coupled, symmetric resonator systems exhibit the phenomena of eigenvalue veering and associated mode localization induced by symmetry breaking parametric changes in the system. This results in orders of magnitude higher sensitivity of mode shapes compared to the sensitivity of resonant frequencies of such systems. Also, their sensitivity varies inversely with the strength of coupling. This opens an alternative sensing paradigm based on mode shapes instead of resonant frequencies. We develop theoretical analysis of mode localization in weakly coupled resonators and validate the results by characterizing purposely designed microelectromechanical (MEMS) devices.
Weakly coupled, symmetric resonator systems exhibit the phenomena of eigenvalue veering and associated mode localization induced by symmetry breaking parametric changes in the system. This results in orders of magnitude higher sensitivity of mode shapes compared to the sensitivity of resonant frequencies of such systems. Also, their sensitivity varies inversely with the strength of coupling. This opens an alternative sensing paradigm based on mode shapes instead of resonant frequencies. We develop theoretical analysis of mode localization in weakly coupled resonators and validate the results by characterizing purposely designed microelectromechanical (MEMS) devices.
[1] Manav, M., Reynen, G., Sharma, M., Cretu, E., & Phani, A. S. (2014). Ultrasensitive resonant MEMS transducers with tuneable coupling. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 24(5), 055005.
[2] Manav, M., Phani, A. S., & Cretu, E. (2017). Mode localized MEMS transducers with voltage-controlled linear coupling. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 27(5), 055010.
[3] Manav, M., Phani, A. S., & Cretu, E. (2018). Mode localization and sensitivity in weakly coupled resonators. IEEE Sensors Journal, 19(8), 2999-3007.
